使用 ProGuard 混淆你的插件
插件混淆已经在官方文档中详细描述,请参阅:obfuscate the plugin
所以,本文将向你展示一个逐步演示,使用 ProGuard 混淆你的插件,从真实示例开始。
要查看比较文件,ProGuard 混淆的关键代码已添加到此 commit,所有代码都在此 repository 中。
添加 ProGuard
Section titled “添加 ProGuard”在 build.gradle.kts 中,添加 buildscript 节点以导入 proguard 依赖项
buildscript { repositories { maven { setUrl("https://maven.aliyun.com/repository/public/") setUrl("https://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public/") setUrl("https://plugins.gradle.org/m2/") setUrl("https://oss.sonatype.org/content/repositories/snapshots/") } mavenCentral() gradlePluginPortal() }
dependencies { classpath("com.guardsquare:proguard-gradle:7.3.2") }}配置 ProGuard
Section titled “配置 ProGuard”在 build.gradle.kts 中注册一个新 task:
// Register a new task, task name is "proguard" register<proguard.gradle.ProGuardTask>("proguard") { dependsOn(instrumentedJar) verbose()
val javaHome = System.getProperty("java.home") File("$javaHome/jmods/").listFiles()!!.forEach { libraryjars(it.absolutePath)}
// Use the jar task output as a input jar. This will automatically add the necessary task dependency. injars("build/libs/instrumented-${properties("pluginName")}-${properties("pluginVersion")}.jar") outjars("build/obfuscated/output/instrumented-${properties("pluginName")}-${properties("pluginVersion")}.jar")
libraryjars(configurations.compileClasspath.get())
dontshrink() dontoptimize()
adaptclassstrings("**.xml") adaptresourcefilecontents("**.xml")
// Allow methods with the same signature, except for the return type, // to get the same obfuscation name. overloadaggressively()
// Put all obfuscated classes into the nameless root package. repackageclasses("") dontwarn()
printmapping("build/obfuscated/output/${properties("pluginName")}-${properties("pluginVersion")}-ProGuard-ChangeLog.txt")
target(properties("pluginVersion"))
adaptresourcefilenames() optimizationpasses(9) allowaccessmodification()
keepattributes("Exceptions,InnerClasses,Signature,Deprecated,SourceFile,LineNumberTable,*Annotation*,EnclosingMethod")
keep(""" class * implements com.intellij.openapi.components.PersistentStateComponent {*;} """.trimIndent() )
keepclassmembers(""" class * {public static ** INSTANCE;} """.trimIndent() ) keep("class com.intellij.util.* {*;}") }
prepareSandbox { if (properties("enableProGuard").toBoolean()) { dependsOn("proguard") pluginJar.set(File("build/obfuscated/output/instrumented-${properties("pluginName")}-${properties("pluginVersion")}.jar")) } }这些是 ProGuard 的语法,更多规则请参阅:Official ProGuard Documentation,我们重点关注最后两个 keep 和 keepclassmembers。
配置完成后,运行插件,调试消息如下:
21:40:12: Executing 'runIde'...
Starting Gradle Daemon...Connected to the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:12563', transport: 'socket'Gradle Daemon started in 915 ms> Task :initializeIntelliJPlugin> Task :patchPluginXml UP-TO-DATE
> Task :verifyPluginConfiguration[gradle-intellij-plugin :verifyPluginConfiguration] The following plugin configuration issues were found:- The Java configuration specifies sourceCompatibility=11 but IntelliJ Platform 2022.3.3 requires sourceCompatibility=17.See: https://jb.gg/intellij-platform-versions
> Task :compileKotlin NO-SOURCE> Task :compileJava UP-TO-DATE> Task :processResources UP-TO-DATE> Task :classes UP-TO-DATE> Task :setupInstrumentCode> Task :instrumentCode UP-TO-DATE> Task :jar UP-TO-DATE> Task :inspectClassesForKotlinIC UP-TO-DATE> Task :instrumentedJar UP-TO-DATE> Task :proguard <=== proguard task 已经成功执行。> Task :prepareSandboxDisconnected from the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:12563', transport: 'socket'Connected to the target VM, address: 'localhost:12616', transport: 'socket'混淆后:
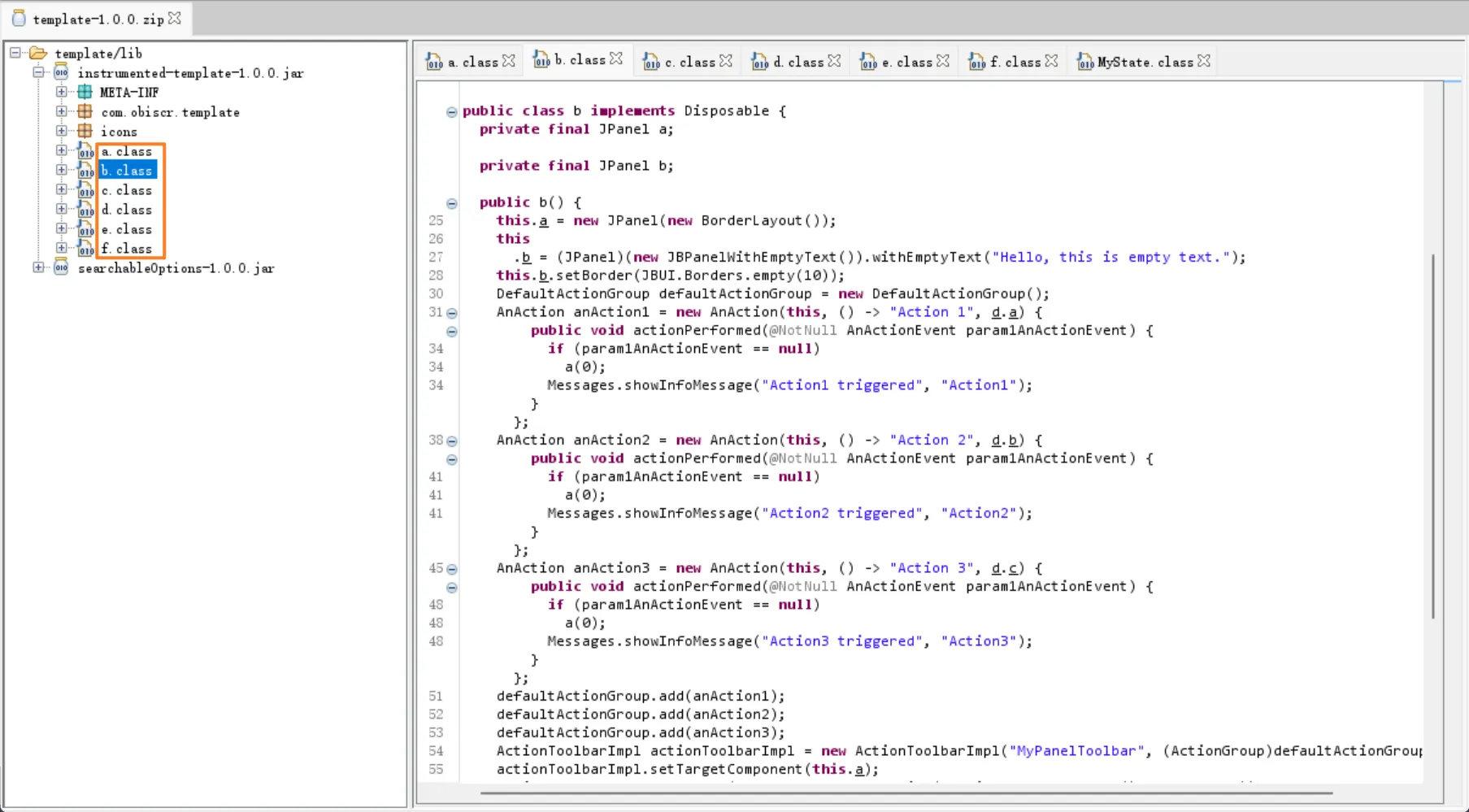
左侧是文件名已混淆,右侧是文件类名、方法名和变量名已混淆。
这只是非常基本的混淆效果,如果你需要更复杂的混淆,可以参考上面提到的 ProGuard 官方文档。
在 IntelliJ 插件项目中,有一些文件不需要混淆。本演示中列出了两个案例。
通过反射调用
Section titled “通过反射调用”项目中的一个文件是 MyDefaultFileType.java。这个文件添加了一个新的文件类型,我们称之为 J-file,具有 *.j 或 *.J 文件扩展名。
这个文件已经在 plugin.xml 中注册
<extensions defaultExtensionNs="com.intellij"> ... <fileType name="MyNativeFile" implementationClass="com.obiscr.template.MyDefaultFileType" fieldName="INSTANCE" extensions="j;J" order="first"/> ...</extensions>关键点是 fieldName 属性:INSTANCE,它对应于 MyDefaultFileType.java 中的 INSTANCE。换句话说,它们必须相同。否则,当反射调用时,属性将找不到。
例如,一旦我们删除了 proguard task 的
register<proguard.gradle.ProGuardTask>("proguard") { ...
// keepclassmembers(""" // class * {public static ** INSTANCE;} // """.trimIndent() // ) ... }
运行插件并获取错误:
2023-09-24 21:31:18,647 [ 3018] WARN - #c.i.e.RunManager - Must be not called before project components initializedInfo | RdCoroutineScope | 53:DefaultDispatcher-worker-35 | RdCoroutineHost overridden2023-09-24 21:31:21,580 [ 5951] SEVERE - #c.i.o.f.i.FileTypeManagerImpl - INSTANCEjava.lang.NoSuchFieldException: INSTANCE at java.base/java.lang.Class.getDeclaredField(Class.java:2610) at com.intellij.openapi.fileTypes.impl.FileTypeManagerImpl.instantiateFileTypeBean(FileTypeManagerImpl.java:492) at com.intellij.openapi.fileTypes.impl.FileTypeManagerImpl.mergeOrInstantiateFileTypeBean(FileTypeManagerImpl.java:463)这表明 INSTANCE 属性找不到。因此,对于这种情况,你可以使用 proguard 的 keepclassmembers 来保持 INSTANCE 属性在所有类中不被混淆。当然,如果你愿意,你也可以保持 INSTANCE 在所有实现 INativeFileType 的类中不被混淆。这是一种更精确的控制。
你可能想知道,既然这个问题可以通过在 plugin.xml 中将 fieldName 与 MyDefaultFileType.java 中的 INSTANCE 保持相同来避免,为什么不通过将它改为相同的值来避免这个问题?

是的,这在原则上是可以的。然而,混淆每次都会生成一个随机变量名。也就是说,属性 fieldName 必须首先被指定为某个确切的值,然后开始打包,在打包后的类文件中,INSTANCE 不一定是上面指定的值。因此,我们仍然需要从混淆规则中排除 INSTANCE 以避免这个问题。
本地数据存储
Section titled “本地数据存储”在许多情况下,需要存储一些本地数据,例如设置数据、环境数据等。在这种情况下,你需要使用 @State 来指定一个文件来存储数据。在这种情况下,你需要使用 @State 来指定存储文件。例如,
package com.obiscr.template;
import com.intellij.openapi.components.*;import com.intellij.openapi.project.Project;import com.intellij.util.xmlb.XmlSerializerUtil;import org.jetbrains.annotations.NotNull;import org.jetbrains.annotations.Nullable;
@State( name = "com.obiscr.template.MyState", storages = @Storage("my-state/state.xml"))public class MyState implements PersistentStateComponent<MyState> { public String currentVersion = ""; public Boolean enableFeature = true; public String myCustomKey = "";
public static MyState getInstance(@NotNull Project project) { return project.getService(MyState.class); }
@Nullable @Override public MyState getState() { return this; }
@Override public void loadState(@NotNull MyState state) { XmlSerializerUtil.copyBean(state, this); }
}这里定义了一个存储文件和一些属性,它将在项目 .idea 目录的 my-state 目录中创建一个新 state.xml 文件,内容如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><project version="4"> <component name="com.obiscr.template.MyState"> <option name="currentVersion" value="v1.0.1" /> <option name="enableFeature" value="false" /> <option name="myCustomKey" value="value" /> </component></project>同样,这里的 option 中的 name 属性对应于 MyState.java 中的三个属性。这些属性不应该被混淆;如果它们被混淆,原始数据将不会被读取。例如,如果你设置:
- currentVersion: v1.0.1
- enableFeature:false
- myCustomKey:value
混淆后,假设 MyState.java 中有以下属性:
- currentVersion -> a
- enableFeature -> d
- myCustomKey -> c
state.xml 中的数据无法读取。因为 option 中没有 name 是:a, d, c 的数据,所以最终读取出的值是 MyState.java 中定义的默认值,一旦这个值发生变化,将在 xml 中再次添加一个新属性。name 是混淆后的变量名。
现在 currentVersion 已经被混淆为 a,所以如果 currentVersion 的值发生变化,将其更改为 v1.0.2,那么 state.xml 将如下所示
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><project version="4"> <component name="com.obiscr.template.MyState"> <option name="currentVersion" value="v1.0.1" /> <option name="enableFeature" value="false" /> <option name="myCustomKey" value="value" /> <!-- Added --> <option name="a" value="v1.0.2" /> </component></project>将添加一个 <option name="a" value="v1.0.2" />。因此,只要混淆后的变量名不同,它就会继续添加。所以这里有一个解决方法:
register<proguard.gradle.ProGuardTask>("proguard") { ...
keep(""" class * implements com.intellij.openapi.components.PersistentStateComponent {*;} """.trimIndent() ) ... }这个规则忽略所有实现 PersistentStateComponent 的类。
本文简要介绍了如何使用 ProGuard 混淆 IntlliJ 插件并将其集成到 gradle 任务中。
实际上,我更喜欢称之为一个框架。具体的混淆规则需要根据你自己的项目进行定制。我希望它能帮助你。
这只是一个研究项目,请根据你自己的项目使用。
我不会对使用这种混淆方案造成的任何损害负责。